Suture Science: Unveiling the Innovations Shaping the Future of Wound Closure
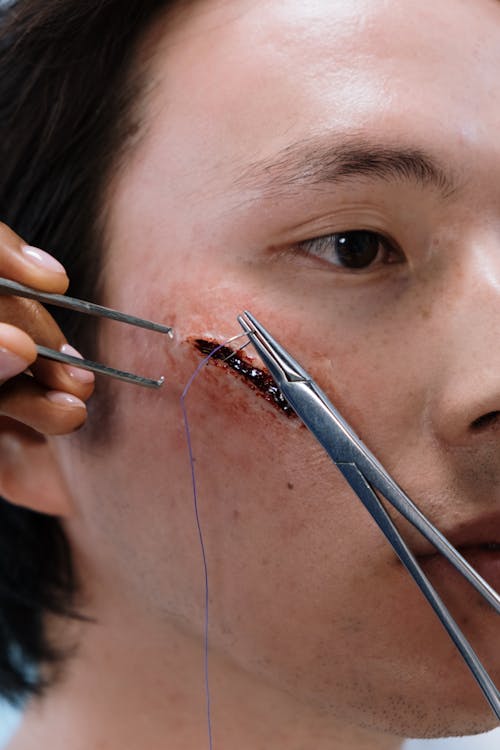
Wound closure is a critical aspect of medical care, and advancements in suture science continue to revolutionize the field. From materials and techniques to technologies and bioengineering, the future of wound closure holds exciting possibilities. In this blog post, we will explore the cutting-edge innovations that are shaping the future of wound closure. By delving into novel suture materials, advanced suturing techniques, and emerging technologies, we will uncover the transformative potential of these innovations in improving patient outcomes and revolutionizing the field of wound closure.
Bioabsorbable and Biocompatible Sutures
The future of wound closure lies in bioabsorbable and biocompatible sutures. These innovative suture materials are designed to degrade within the body, reducing the need for suture removal procedures. Biocompatible sutures minimize tissue reaction and promote better wound healing, ensuring optimal patient outcomes. The development of new biomaterials, such as polycaprolactone and silk-based sutures, showcases the potential for improved biocompatibility and enhanced wound closure techniques.
Tissue-Adhesive Suturing
Tissue-adhesive suturing techniques offer a minimally invasive alternative to traditional sutures. These adhesives, such as cyanoacrylate-based glues or fibrin sealants, provide strong and reliable wound closure by bonding the tissue edges together. Tissue-adhesive suturing eliminates the need for needles, reducing patient discomfort and potentially improving cosmetic outcomes. This technology holds promise for a wide range of applications, from small superficial wounds to complex surgical procedures.
3D Printing of Suture Materials
Advancements in 3D printing technology are transforming the production of suture materials. Customized sutures with specific properties can be designed and printed, allowing for tailored wound closure based on patient needs. 3D-printed sutures offer enhanced strength, flexibility, and biocompatibility, resulting in improved wound closure and reduced postoperative complications. This innovation holds great potential for personalized medicine and the optimization of wound closure techniques.
Surgical Robotics and Automation
Surgical robotics and automation are rapidly advancing, bringing precision and efficiency to the field of wound closure. Robotic-assisted suturing systems, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, enhance surgeon dexterity and provide real-time imaging for precise suturing. Additionally, automated suturing devices streamline the suturing process, reducing procedure time and improving overall outcomes. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into robotic systems further augments their capabilities and opens new avenues for innovation in wound closure.
Nanotechnology and Drug-Loaded Sutures
Nanotechnology holds promise for the future of wound closure by incorporating drug delivery systems into sutures. Drug-loaded sutures enable localized delivery of therapeutic agents, such as antimicrobial or anti-inflammatory substances, directly to the wound site. This technology can help prevent infections, accelerate healing, and reduce the risk of complications. The development of nanofiber-based sutures and coatings with controlled drug release profiles showcases the potential of this innovative approach.
Conclusion
The future of wound closure is driven by the continuous advancement of suture science. Bioabsorbable and biocompatible sutures, tissue-adhesive techniques, 3D printing of suture materials, surgical robotics and automation, and drug-loaded sutures are just a few of the innovations shaping the field. These advancements hold great promise for improved patient outcomes, reduced complications, and enhanced wound healing. As researchers, engineers, and medical professionals collaborate to push the boundaries of suture science, we can anticipate a future where wound closure techniques are increasingly tailored, precise, and patient-centric, transforming the landscape of healthcare.
