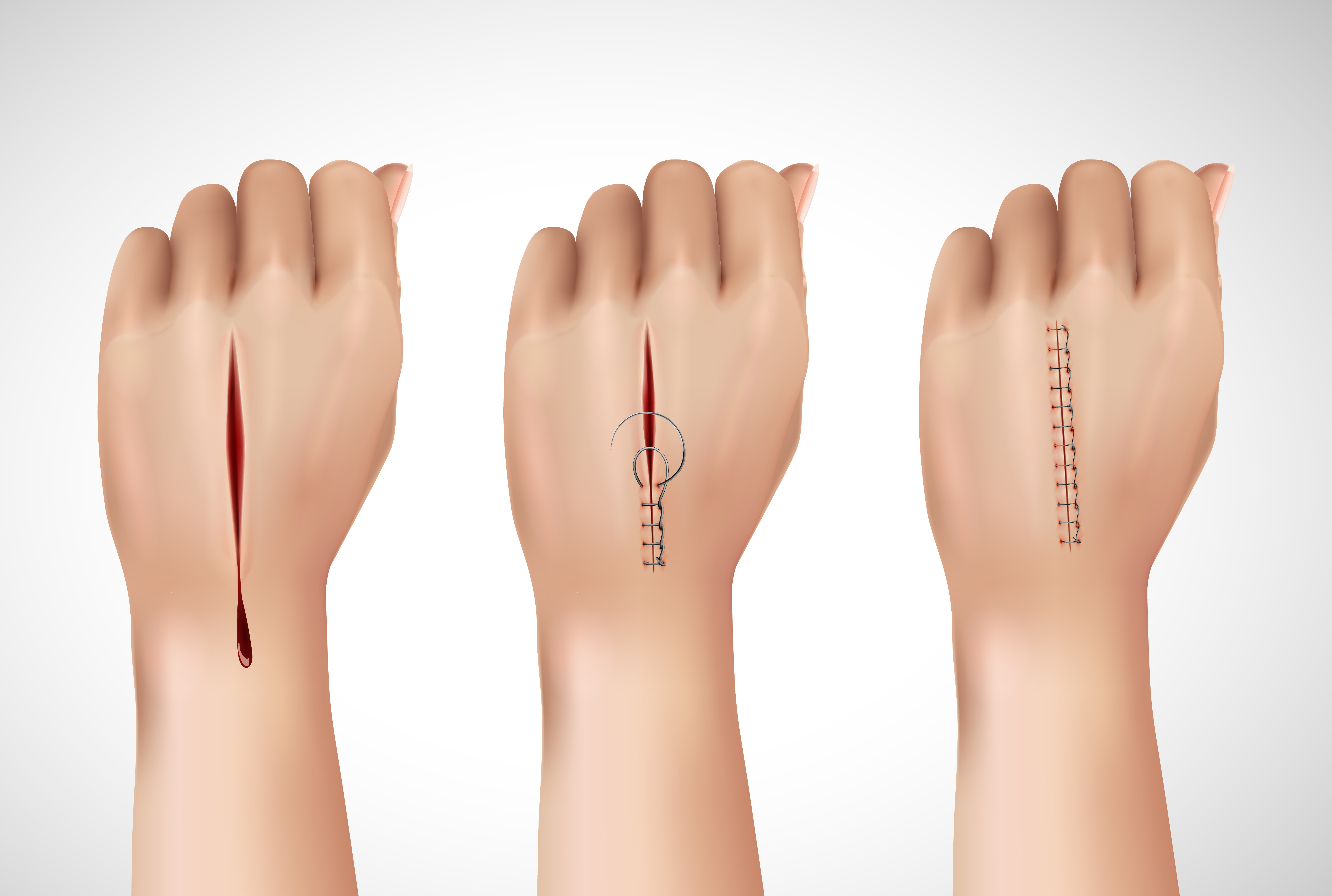
Sutures, an essential component of wound closure, come in various materials that cater to different surgical needs. Understanding the science behind these materials is crucial for surgeons and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions about the most suitable suture for each patient’s unique circumstances. We will explore the science behind two primary categories of sutures: absorbable and non-absorbable, delving into their composition, properties, and applications.
![]() Absorbable Sutures: Nature’s Safe Decomposers
Absorbable Sutures: Nature’s Safe Decomposers
a. Composition: Absorbable sutures are made from biodegradable materials that naturally break down in the body over time. The two most common types of absorbable sutures are polyglycolic acid (PGA) and polylactic acid (PLA). PGA sutures boast excellent initial strength but degrade rapidly, typically within 10 to 14 days. PLA sutures, on the other hand, have a slower degradation rate, lasting between 45 to 90 days. Other absorbable materials include polydioxanone (PDO), which provides a more prolonged tensile strength, degrading over several months.
b. Properties and Applications: Absorbable sutures are ideal for internal wound closure, where the sutures are not meant to be removed after healing. They are commonly used in deep tissue layers, such as for closing the muscle layers during abdominal surgeries or repairing internal organs. The controlled degradation of these sutures ensures that they maintain wound support during the critical healing period and gradually lose strength as the tissue regains its strength.
![]() Non-Absorbable Sutures: Lasting Support for External Wounds
Non-Absorbable Sutures: Lasting Support for External Wounds
a. Composition: Non-absorbable sutures are made from synthetic materials that resist biodegradation and remain in the body indefinitely. Common non-absorbable sutures include nylon, polypropylene, and silk. These sutures exhibit high tensile strength and resist degradation by enzymes, making them suitable for external wounds that require long-term support.
b. Properties and Applications: Non-absorbable sutures are typically used for wound closure in superficial layers, such as the skin. Due to their durability, they provide long-lasting support for wounds that take a more extended period to heal. These sutures are often used in situations where removal is necessary, such as skin closures after surgery or certain types of injuries.
![]() Factors Influencing Suture Selection
Factors Influencing Suture Selection
Several factors influence the selection of the most appropriate suture material for a particular surgical procedure or wound closure:
a. Wound Location and Type: The depth and location of the wound, as well as the type of tissue being sutured, play a crucial role in determining whether an absorbable or non-absorbable suture is more suitable.
b. Healing Time: The expected healing time of the wound is a critical consideration. Absorbable sutures are preferred for wounds that heal relatively quickly, while non-absorbable sutures are used for wounds that may require more extended support.
c. Tensile Strength: The tensile strength of the suture material should match the requirements of the wound. Internal tissues may require sutures with higher initial strength, while external wounds might benefit from sutures with prolonged strength.
d. Allergies and Reactions: Some patients may have allergies or adverse reactions to specific suture materials, making it necessary to consider alternative options.
![]() Conclusion
Conclusion
Suture materials are a critical aspect of wound closure, and understanding the science behind absorbable and non-absorbable options is essential for making informed decisions in surgical settings. Absorbable sutures provide controlled support during the healing process, gradually degrading as the wound heals. On the other hand, non-absorbable sutures offer long-term support for external wounds that take longer to heal.